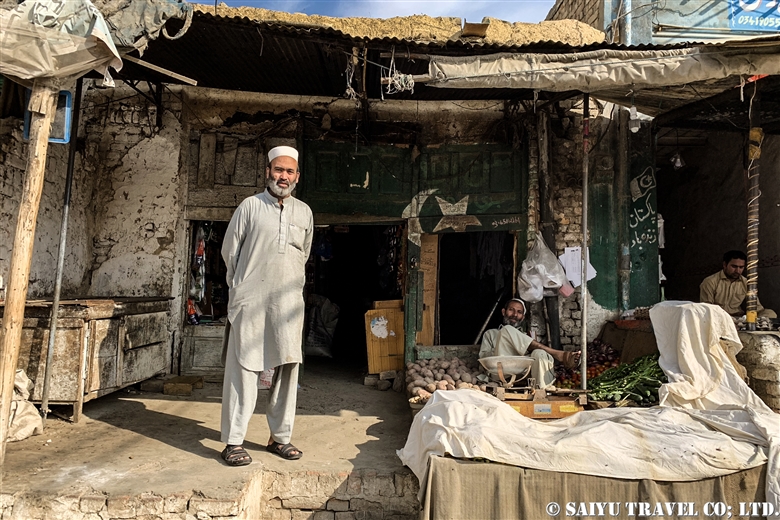
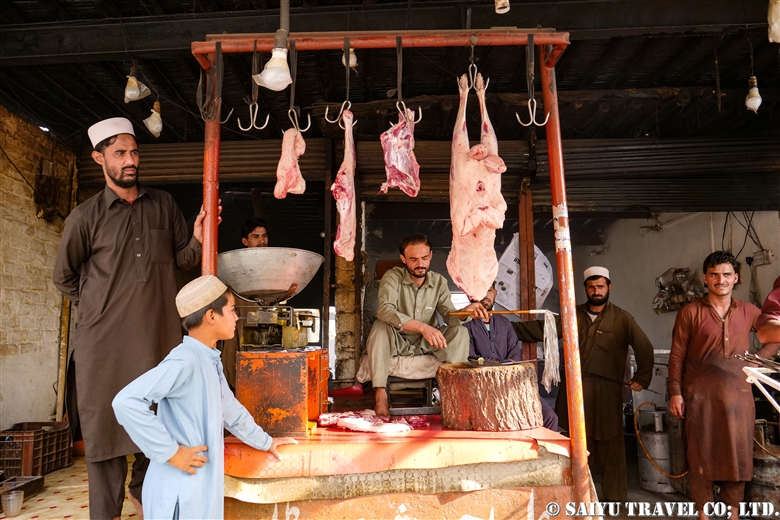
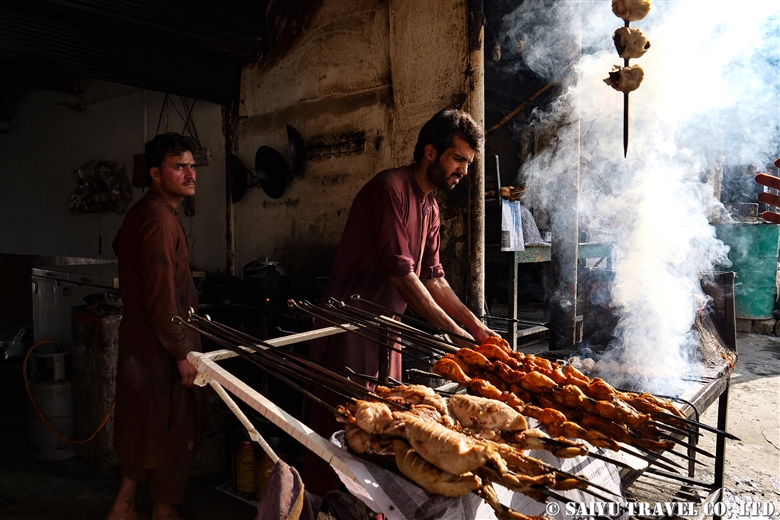
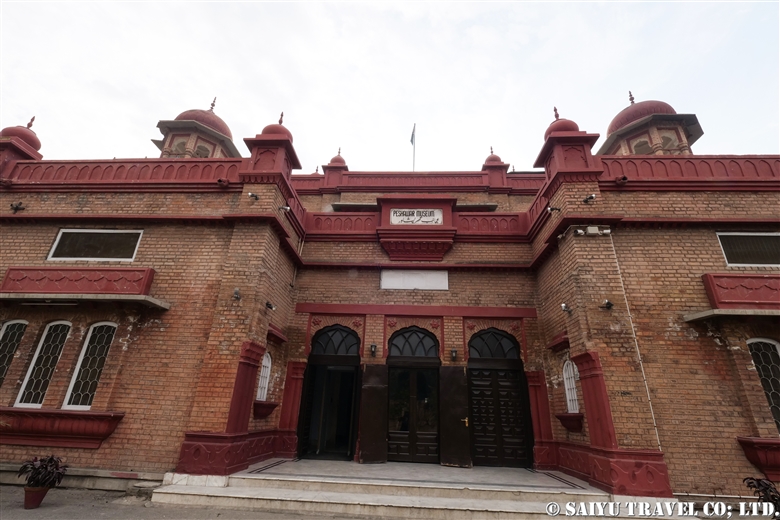
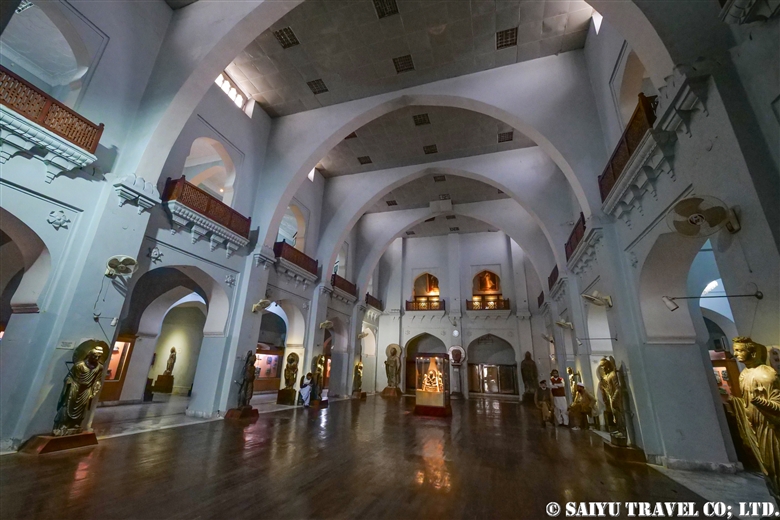
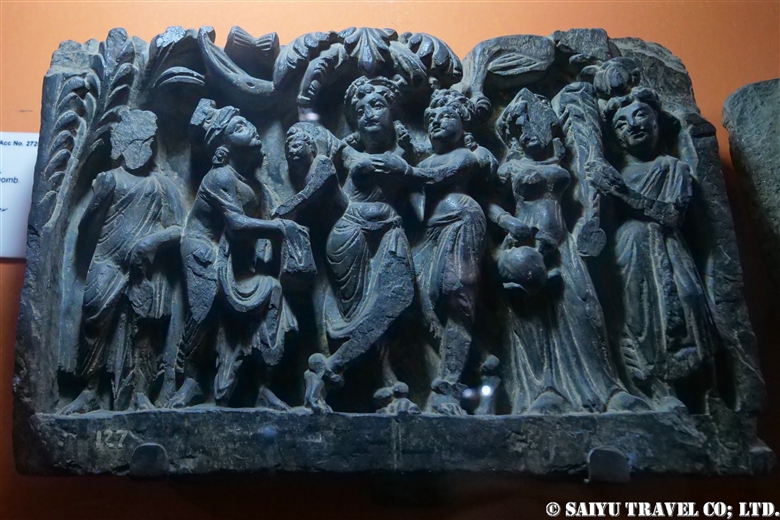
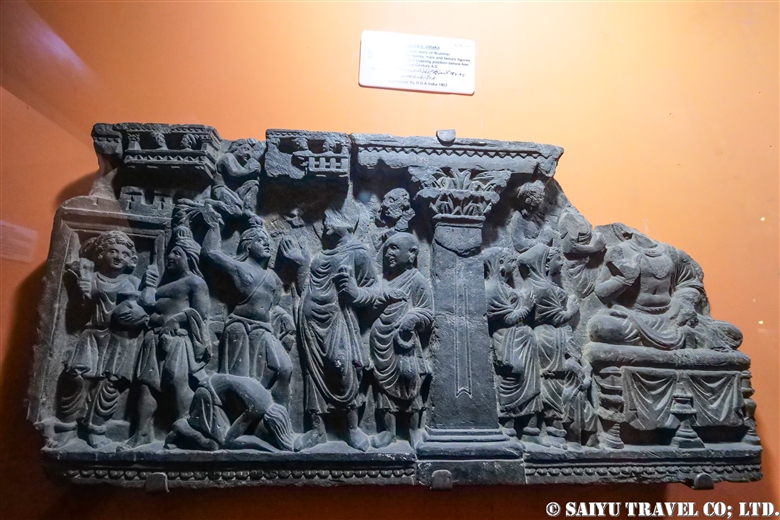
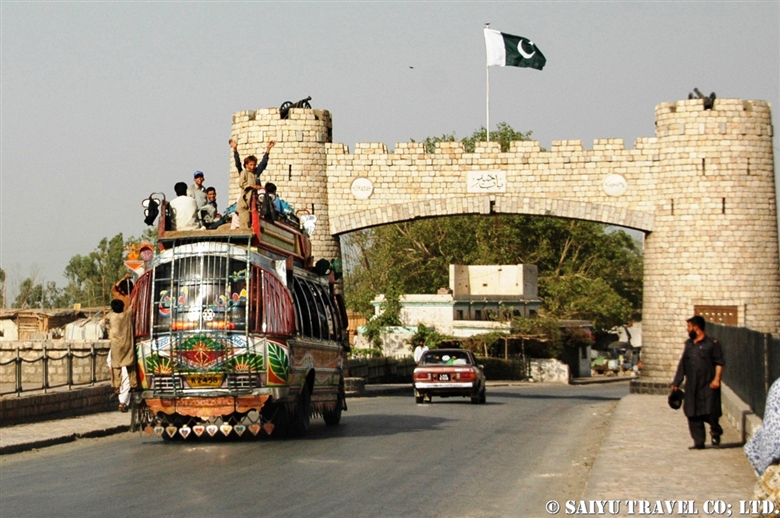
One of the places where it is very difficult to get an entry permit is the Khyber Pass. It is right on the border with Afghanistan, located in the former tribal area on the road leading to Torkham. In 2018, it was transferred to Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, but it is still one of the more difficult places to visit.
The historic Khyber Pass has been an important trade route connecting the eastern and western cultures. The Sulaiman mountains on the border are where Alexander the Great’s army, and the Chinese Buddhist Scholar, Xuanzang (In Japanese known as Genjō) crossed here. During the Mughal Dynasty, it was developed as the Grand Trunk Road running from India to Kabul in Afghanistan. It also became a significant battlefield from the First British War to the independence of Pakistan in modern times. After Pakistan’s independence it became a tribal area.
For travelers, it is an exciting part of history and romance as a pass that connects the “Central Asian world” and the “Indian world”.
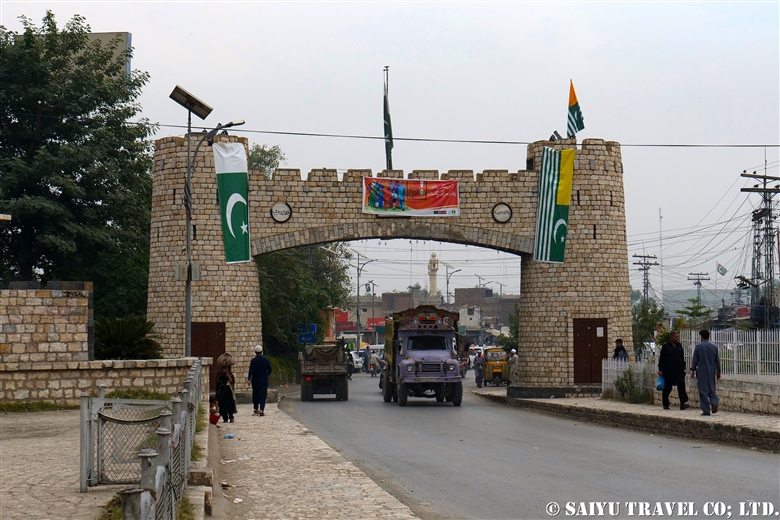

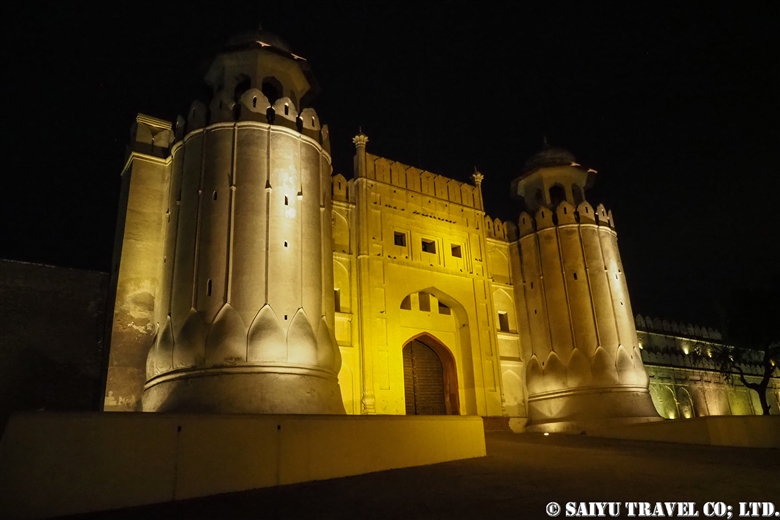
The first monument from Peshawar to Khyber Pass is this Khyber Gate ‘Bab-e- Khyber’. Peshawar was already quite a busy town, but the tram in the middle of the main road made the road even narrower and the traffic was horrible.
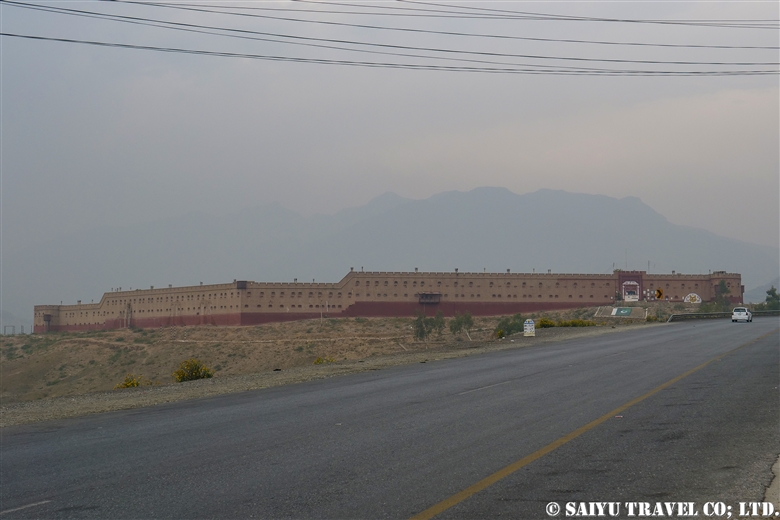

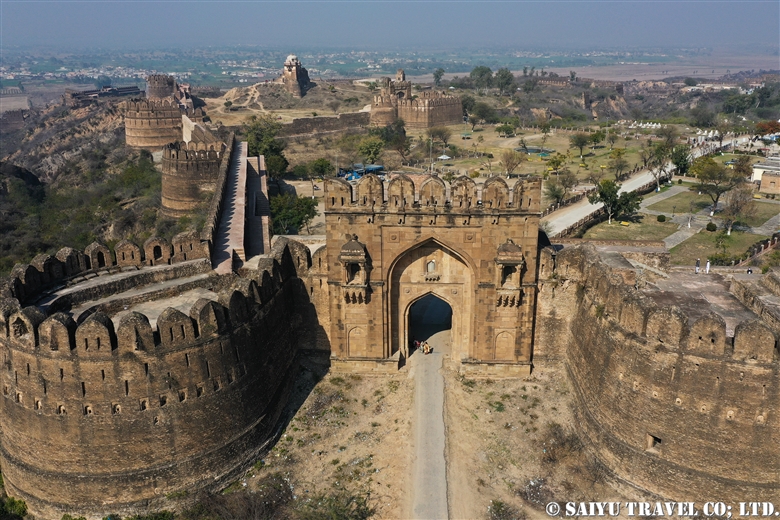
The giant Shagai Fort was built by the British Army in 1920 and is now used by the Pakistani Army.
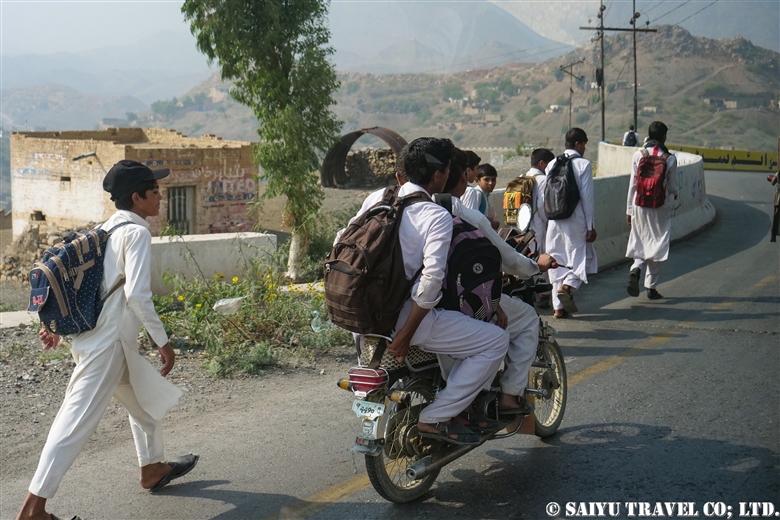

Students who we passed along the road. These students commuting to school was really refreshing in the old tribal area.
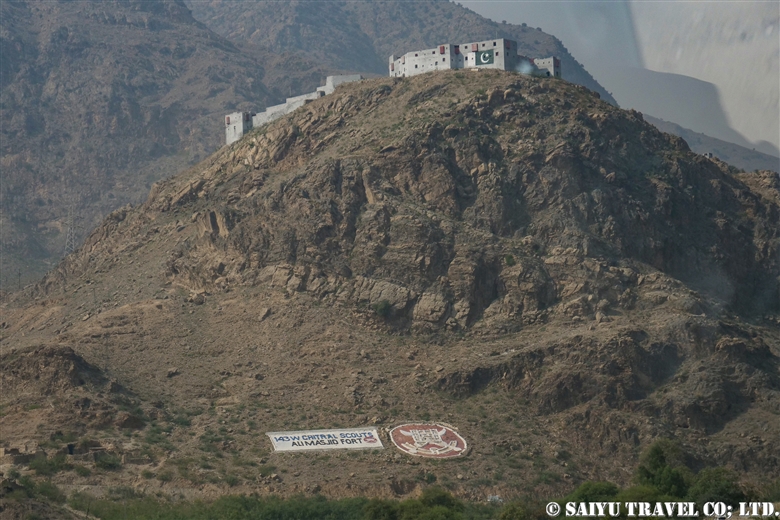

This was the narrowest place of the Khyber Pass road, mountains on both sides, and for that it became a strategically important position. It a fierce battlefield during many wars. This is the Ali Masjid Mosque and on the hill is the Pakistani military fortress Ali Masjid Fort.
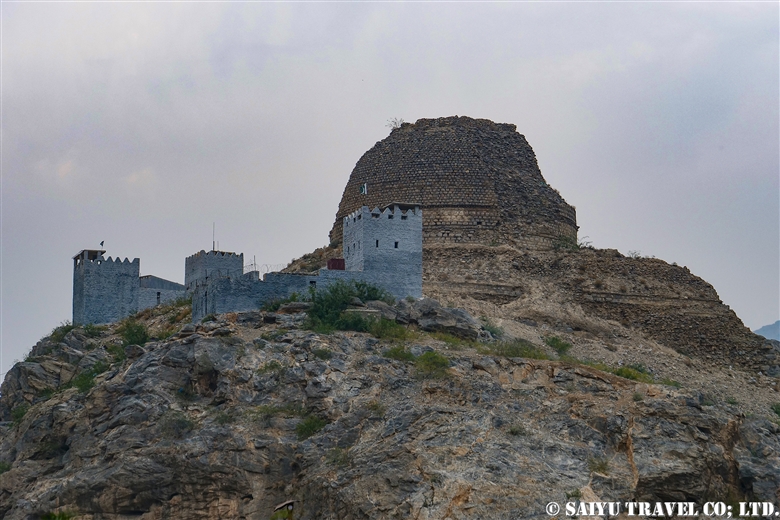

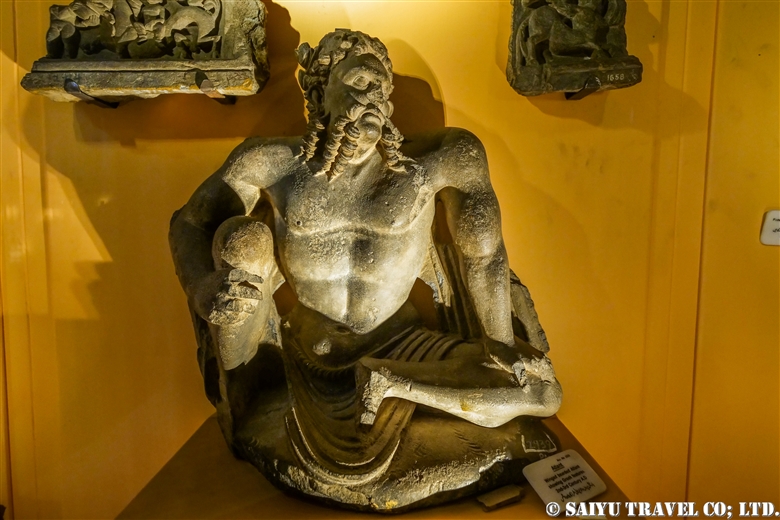
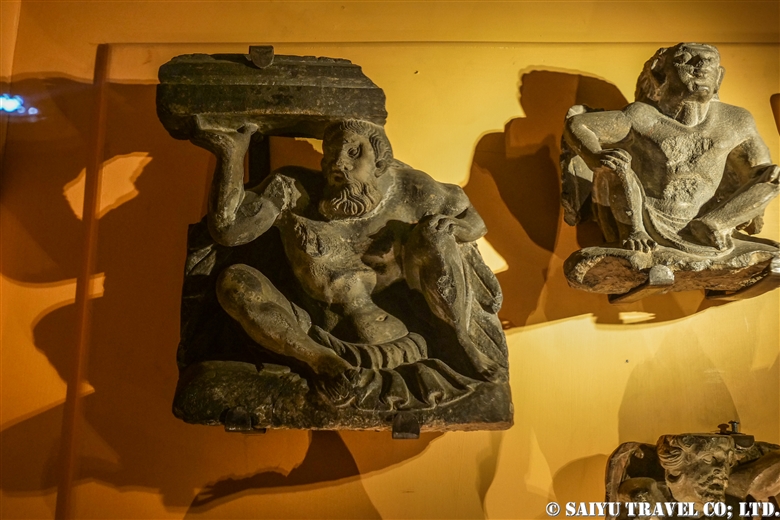
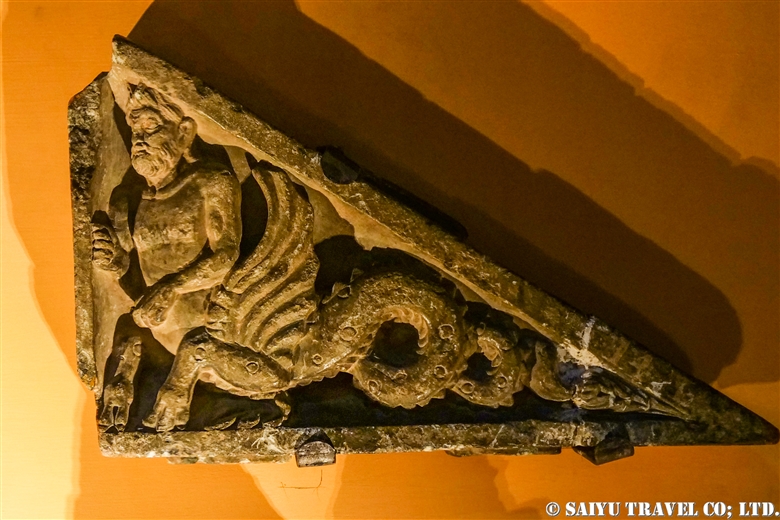
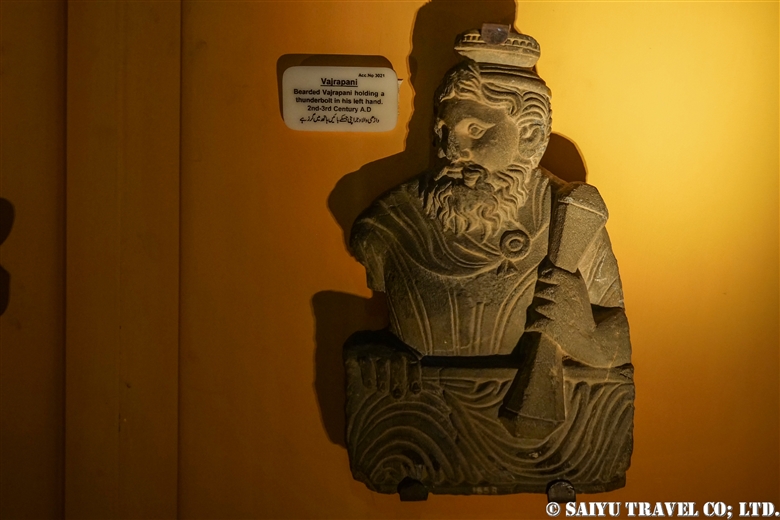
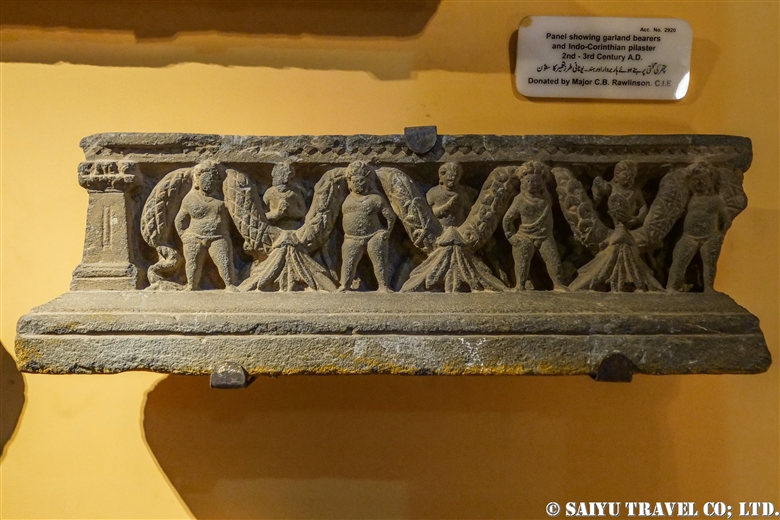
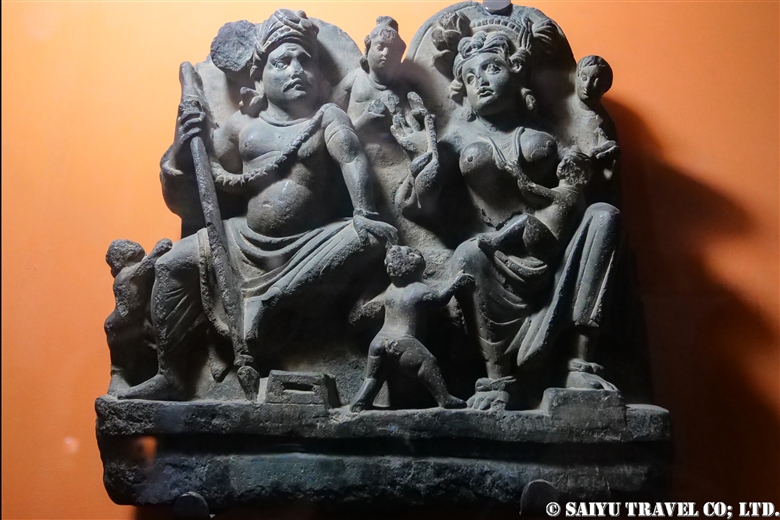
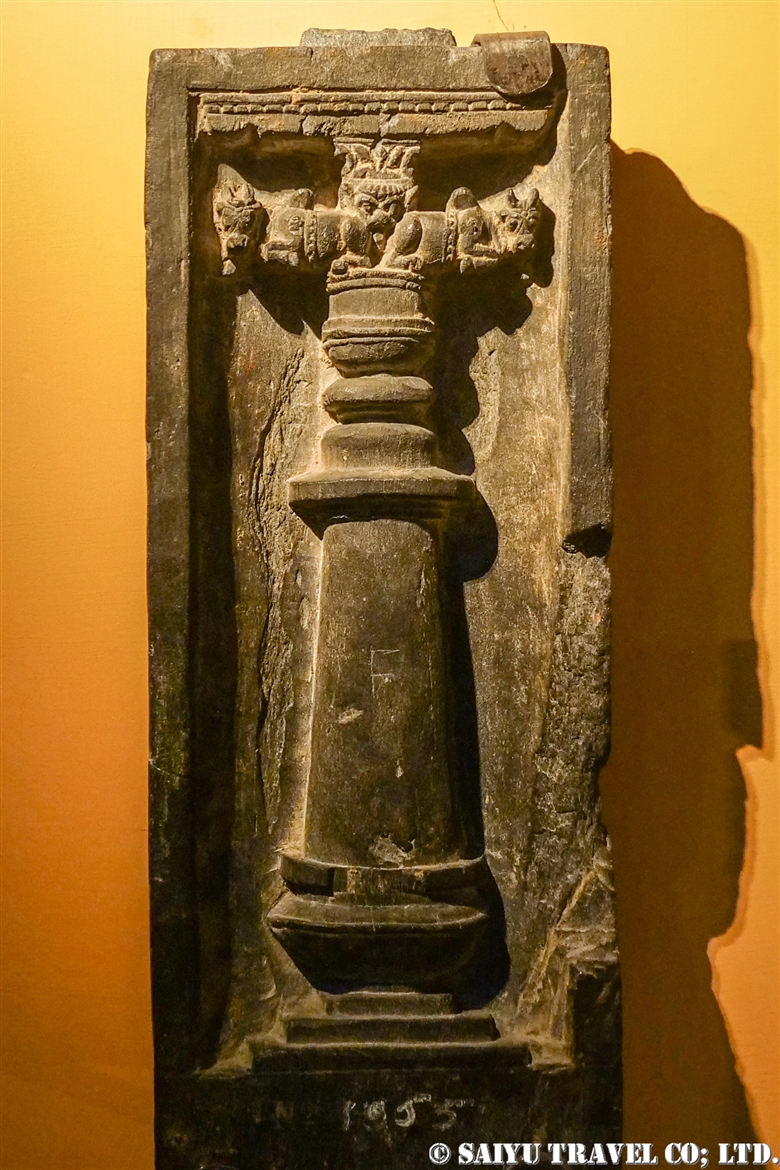
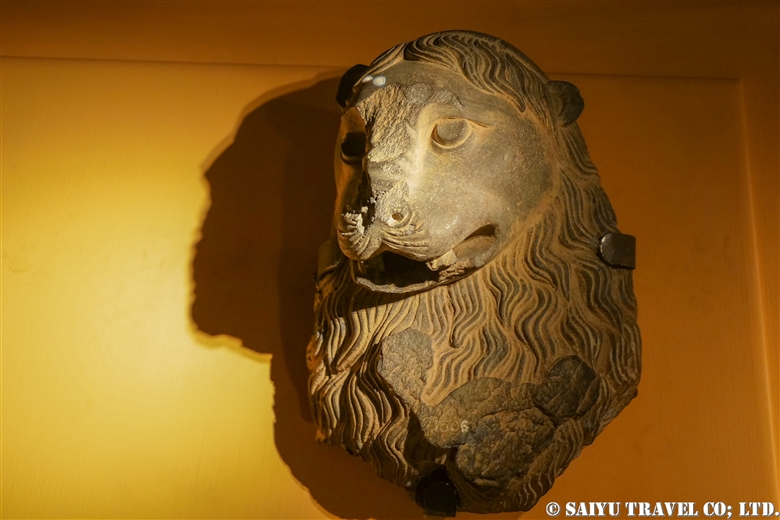
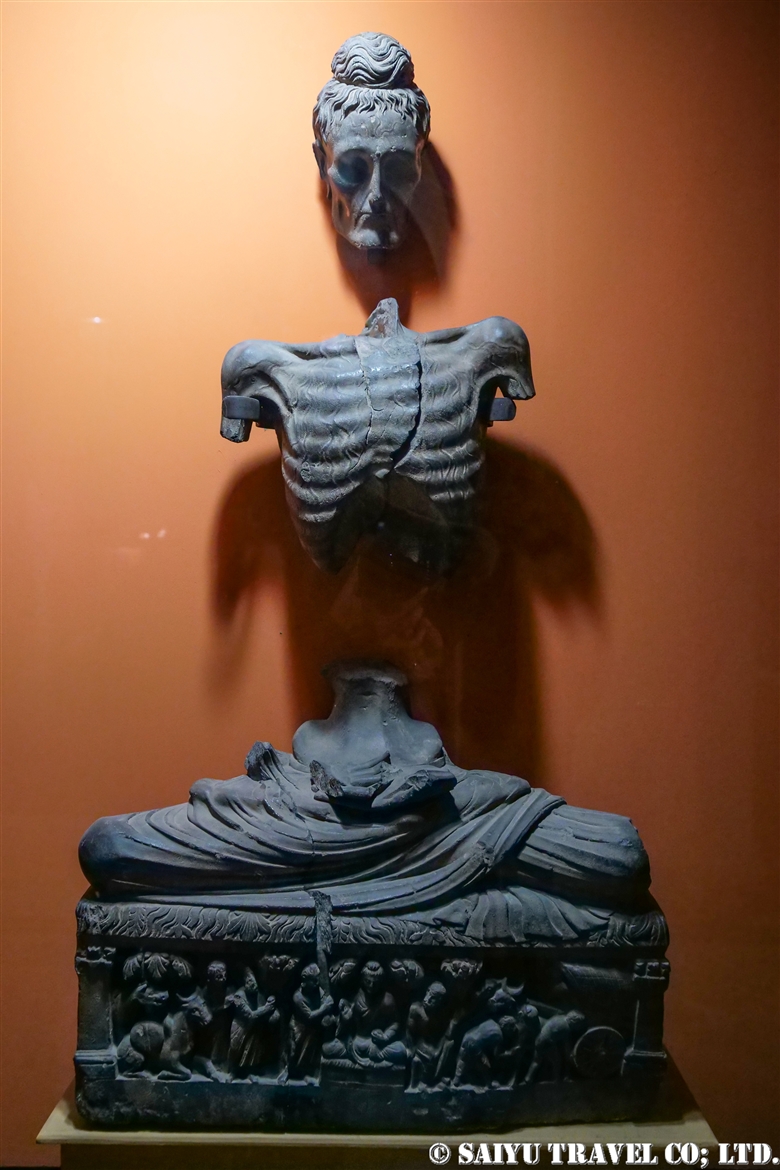
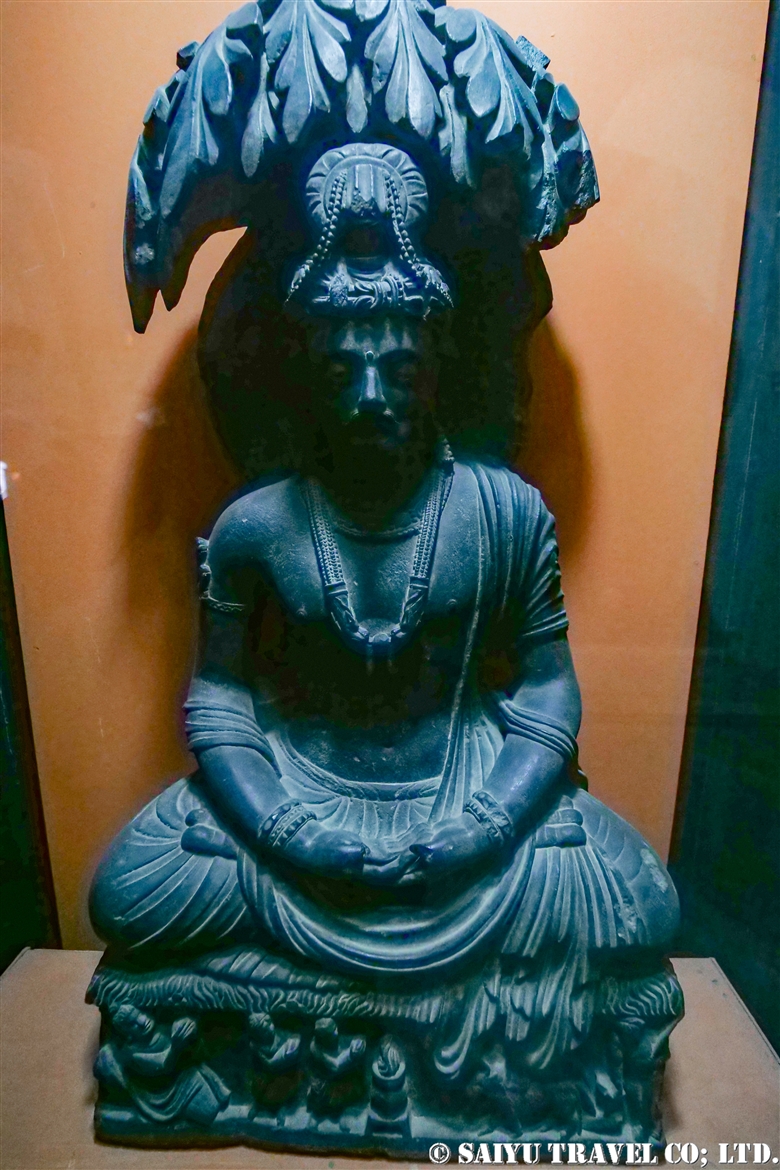
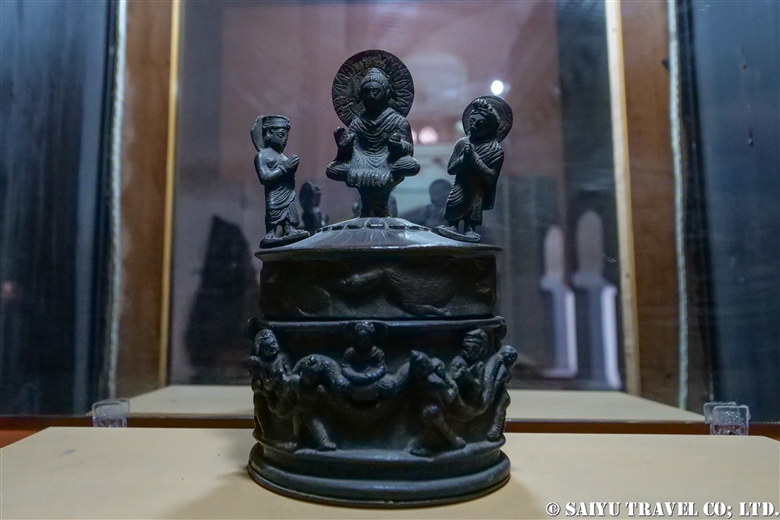
One of the most shocking things we learned was that the fortress was built beside buddhist stupa of Kushan Empire, which amazingly dates back to the 2nd and 5th centuries.
This is Sphola Stupa sits on a three-story platform. It housed some Gandhara sculptures, Buddha statues that were excavated in the early 20th century.
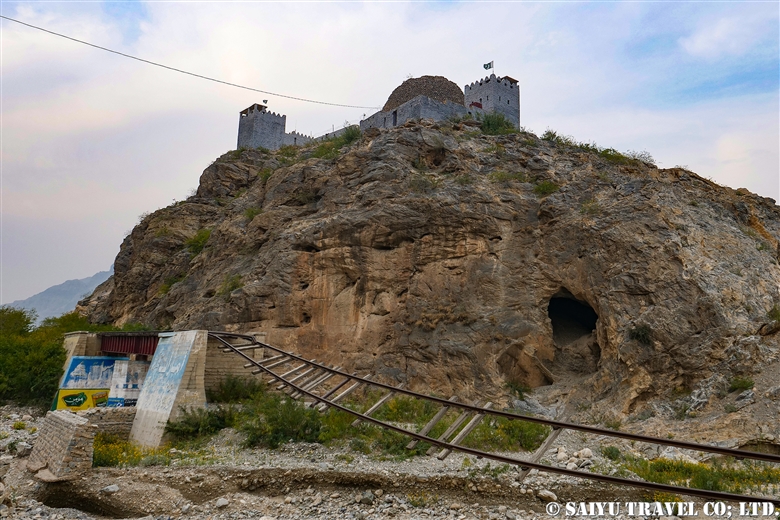

The other shocking thing is the miserable state of this “Khyber Railway” track. It is such a pity because I expected that the “Khyber Railway” steam locomotive would be revived to invigorate the domestic tourism.
The railroad was originally opened in 1926, while under British rule for the purpose of transporting military supplies. The trip from Peshawar to Landi Kotal, which is 34 kilometers long and rises in elevation by 600 meters, crosses 34 tunnels and 92 iron bridges, and the steam locomotive trip here was one of the highlights of tourism.
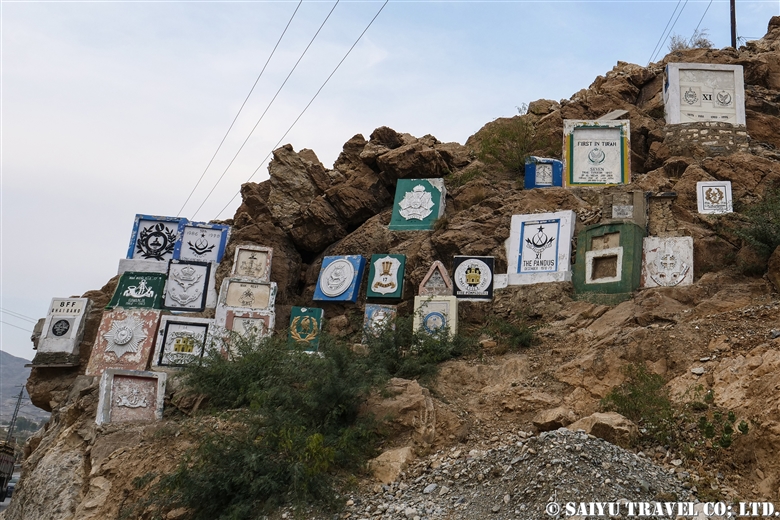

It is said that the military from various times and various countries that passed through this area have carved their coat of arms on the rock surface as a memorial.
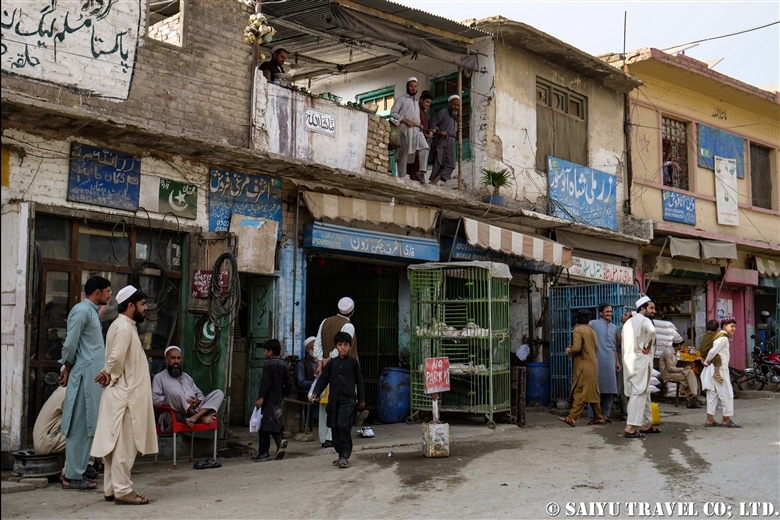

Then we passed through the Landi Kotal market. This was once a famous place for the smuggling trade.
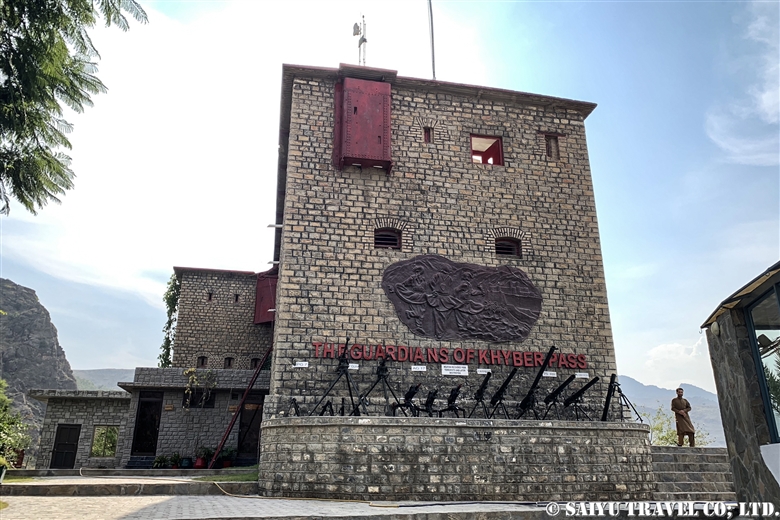

This is the Michni Checkpost where “The Guardians of Khyber Pass” overlook the Pakistani border with Afghanistan. The observatory serves as a lookout post over at Afghanistan.
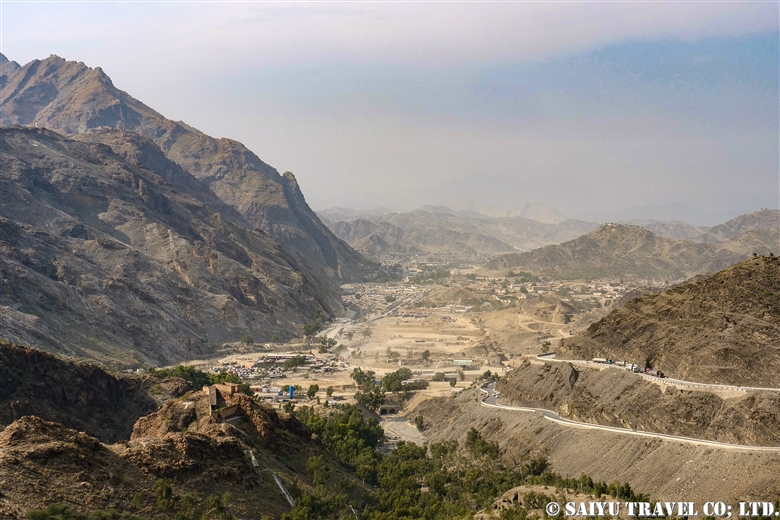

A view of Afghanistan from the Michni Checkpost. In the valley, there are immigration and customs offices of both countries, and passing through here, will take you to Torkham.
Click here for more information on Khyber Pass (It was written based on photos from around 2008. Please compare it with the old photo and see how it has changed.)
Photo & text : Mariko SAWADA
※These photos were taken in October 2019 during the visit.
Tag : Khyber Pass , Indus Caravan , Bab-e-Khyber , Saiyu Travel , Shagai Fort , Saiyu Travel Pakistan , Ali Masjid , Pakistan Travel company , Landi Kotal , Pakistan Photography Tour , Michni Checkpost , Peshawar , Torkham , Khyber Gate , Pakistan Heritage Tour , Pakistan Blog , Pakistan Travel Blog , Gandhara tour